Allergy Patch Tests Food

Mar 12, 2014 Allergy testing involves having a skin or blood test to find out what substance, or allergen, may trigger an allergic response in a person. Skin tests are.

Patch Testing Advanced Allergy Asthma Associates/Food Allergy Center of Illinois uses various techniques for diagnosing allergies. In many cases, a simple procedure.

Patch tests contact allergy testing Dermatologists apply patch tests in patients with dermatitis, to find out whether their skin condition may be caused or.
Allergy tests Overview covers definition, risks, results of skin tests for allergic sensitivities.
Food Patch Testing: Food patch testing is used to detect possible food allergies. This test differs from ImmunoCap blood tests or skin prick tests, which are used to.
Food patch testing is used to detect possible food allergies. This test differs from ImmunoCap blood tests or skin prick tests, which are used to evaluate for.
Patch Testing. A patch test is used to find allergic causes of eczema/dermatitis and some other types of skin reactions such as reactions to drugs.
Allergy testing involves having a skin or
blood test to find out what substance, or
allergic response in a person. Skin tests are usually
done because they are rapid, reliable, and generally less expensive than blood
tests, but either type of test may be used.
A small amount of a suspected allergen
is placed on or below the skin to see if a reaction develops. There are three
test is done by placing a drop of a solution containing a possible allergen on
the skin, and a series of scratches or needle pricks allows the solution to
enter the skin. If the skin develops a red, raised itchy area called a wheal,
it usually means that the person is allergic to that allergen. This is called a
this test, a small amount of the allergen solution is injected into the skin.
An intradermal allergy test may be done when a substance does not cause a
reaction in the skin prick test but is still suspected as an allergen for that
person. The intradermal test is more sensitive than the skin prick test but is
more often positive in people who do not have symptoms to that allergen false-positive test results.
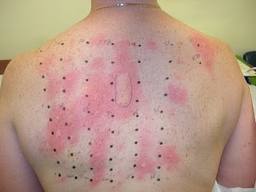
Skin patch test. For a skin patch test, the allergen solution
is placed on a pad that is taped to the skin for 24 to 72 hours. This test is
used to detect a skin allergy called
substances in the blood called
antibodies. Blood tests are not as sensitive as skin
tests but are often used for people who are not able to have skin tests.
The most common type of blood test used is the enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay ELISA, EIA. It measures the blood level of a type of
antibody called immunoglobulin E, or IgE that the body may make in response
to certain allergens. IgE levels are often higher in people who have allergies
Other lab testing methods, such as radioallergosorbent
testing RAST or an immunoassay capture test ImmunoCAP, UniCAP, or Pharmacia
CAP, may be used to provide more information.
Your allergy test results may show that allergy
treatment is a choice for you. For more information, see:
Allergies: Should I Take Allergy Shots.
Health Tools help you make wise health decisions or take action to improve your health.
Decision Points focus on key medical care decisions that are important to many health problems.
Allergy testing is done to find out what
substances allergens cause an allergic reaction.
WebMD Medical Reference from Healthwise
This information is not intended to replace the advice of a doctor.
Healthwise disclaims any liability for the decisions you make based on this
1995-2011 Healthwise, Incorporated. Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated.
The skin prick test can also be done
Identify inhaled airborne allergens, such
as tree, shrub, and weed pollens, molds, dust, feathers, and pet
Identify likely food allergens such as eggs, milk,
peanuts, nuts, fish, soy, wheat, or shellfish.
A blood test on a blood sample may be
done instead of a skin prick test if a person:
hives or another skin condition, such as
eczema, that makes it hard to see the results of skin
Cannot stop taking a medicine, such as an
antihistamine or tricyclic antidepressant, that may
prevent or reduce a reaction to a substance even when a person is allergic to
Has had a severe allergic reaction anaphylaxis.
to many foods. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay ELISA can find out the foods
that a person is most allergic to.
Many medicines can affect the results of
a skin test. Be sure to tell your doctor about all the
nonprescription and prescription medicines you take.
You may need to stop taking some medicines, such as some tricyclic
antihistamines such as cetirizine Zyrtec,
fexofenadine Allegra, and loratadine Claritin, before you have an allergy
Talk to your doctor about any concerns
you have regarding the need for the test, its risks, how it will be done, or
what the results will show. To help you understand the importance of this test,
medical test information form What is a PDF document..
The health professional doing the
skin prick or intradermal test will:
Clean the test site usually on your back or
Place drops of the possible allergens on your
many substances to be tested at the same time.
each drop with a needle. The needle passes through the drop and allows some of
the allergen to penetrate your skin. For the intradermal test, a needle is used
to inject the allergen solution deeper into the skin. See a picture of a
Check the skin after 12 to 15 minutes for red,
raised itchy areas called wheals. If a wheal forms, it means you are allergic
to that allergen this is called a positive reaction.
An alternative skin prick method uses a device with 5 to
10 points heads, which are dipped into bottles that contain the allergen
extract. This device is pressed against the skin of the forearm or back so that
all heads are pressed into the skin at the same time.
prick test is negative, you may choose to have an intradermal skin test at a
later visit. A skin prick test is usually done first because the intradermal
test has a greater chance of causing a severe allergic reaction.
The skin prick test and the intradermal test usually take less than an
small doses of the suspected allergen. For this test:
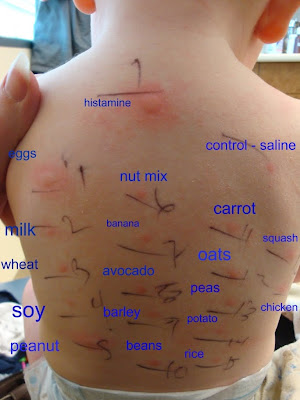
Doses of allergens are placed on patches that
The patches are then placed on the
skin usually on your back. This usually takes about 40 minutes, depending on
how many patches are applied. See a picture of a
You will wear the patches for 24 to 72 hours.
Do not take a bath or shower or do any activities that could make you sweat
excessively while you are wearing the patches. This could loosen the patches
The patches will be removed by your
health professional, and your skin will be checked for signs of an allergic
The health professional drawing your
Wrap an elastic band around your upper arm to stop the flow of
blood. This makes the veins below the band larger so it is easier to put a
Put the needle into the vein. More than one needle stick
Attach a tube to the needle to fill it with
Remove the band from your arm when enough blood is
Apply a gauze pad or cotton ball over the needle site as
Apply pressure to the site and then a
The blood sample will be placed on specially treated
paper and sent to a lab to determine whether
antibodies to any of the allergens being tested are
present. If specific antibodies are found, it may mean you are allergic to a
With the skin prick test and the
intradermal skin test, you may feel a slight pricking sensation when the skin
beneath each sample is pricked or when the needle penetrates your skin.
If you have an allergic reaction from any of the skin tests, you may have
some itching, tenderness, and swelling where the allergen solutions were placed
on the skin. After the testing is done, cool cloths or a nonprescription
steroid cream can be used to relieve the itching and swelling.
you are having a skin patch test and you have severe itching or pain under any
of the patches, remove the patches and call your doctor.
You may feel nothing at all from the
needle puncture, or you may feel a brief sting or pinch as the needle goes
through the skin. Some people feel a stinging pain while the needle is in the
vein. But many people do not feel any pain or have only minor discomfort after
the needle is positioned in the vein.
The major risk with the skin prick test
or the intradermal skin test is a severe allergic reaction called
anaphylaxis. Symptoms of a severe allergic reaction
include itching, wheezing, swelling of the face or entire body, difficulty
breathing, and low blood pressure that can lead to
shock. An anaphylactic reaction can be
life-threatening and is a medical emergency. Emergency care is always needed
for an anaphylactic reaction. But severe allergic reaction is rare, especially
If you are having a skin patch test and
you have severe itching or pain under any of the patches, remove the patches
There is very little risk of a problem
from having blood drawn from a vein.
You may develop a small bruise at the
puncture site. You can reduce the risk of bruising by keeping pressure on the
site for several minutes after the needle is withdrawn.
cases, the vein may become inflamed after the blood sample is taken. This
condition is called phlebitis and is usually treated with a warm compress
Continued bleeding can be a problem
for people with bleeding disorders. Aspirin, warfarin Coumadin, and other
blood-thinning medicines can also make bleeding more likely. If you have
bleeding or clotting problems, or if you take blood-thinning medicine, tell
your doctor before your blood is drawn.
A skin or blood test can tell you what
Skin tests work by exposing a person
to suspected allergens and seeing if a reaction occurs. The results of the skin
tests will be available immediately after testing is done.
No raised red areas called wheals are created by the
A wheal created by the allergen is at least 1/8 inch
3 mm larger than the reaction to the negative control. The larger the wheal,
the more certain it is that the person is allergic to that specific allergen.
substances in the blood called antibodies. Results of allergy blood tests are
usually available in about 7 days.
The levels of immunoglobulin E IgE, a type of
antibody, are the same as in a person who does not
The levels of immunoglobulin E IgE antibodies for a
particular allergen or group of allergens are 4 times the normal level.
Reasons you may not be able to
have a skin test or why the results may not be helpful include:
Exercise that causes excessive
antihistamines or tricyclic antidepressants.