Red Scaly Patch On Arm
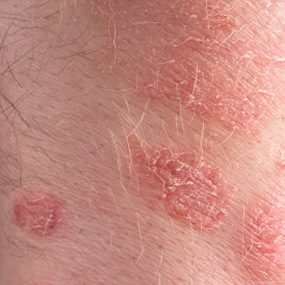
Find the answer to this and other Dermatology questions on JustAnswer. red, flaky non-itching spots on my arms spot to reappear in another. Mainly on arms.
Red Patches on Arms This too does not seem to be raised and is scaly but not flaky. Since the original patch I started out with one red raised patch on my arm.
Scaly Lesions On Arms I have a half circle spot on my arm that is red at times and They are red in color and full of pus and blood and scaly.The.
Scaly Crusted Spots on Scaly Crusted Spots on the Skin - Actinic Keratosis By Dr. Jere Mammino and Dr The longer the spot is frozen the better the chance it.

Psoriasis is a disease which affects the skin and joints and commonly causes red scaly patches to appear on the skin. The scaly patches are areas of inflammation and excessive skin production. Psoriasis can cause pain, itching, burning and emotional distress. It affects both sexes equally and can occur at any age, although it most commonly appears for the first time between the ages of 15 and 25.
Today more than seven million Americans suffer with psoriasis. Recent studies show that there may be an ethnic link. It seems that psoriasis is most common in Caucasians, slightly less in African Americans and far less common among Asians and Native Americans.
Psoriasis is not contagious. You can t catch psoriasis from another person or give it to someone by touching them, and you can t spread it to other parts of your body.
Psoriasis is probably one of the longest known illnesses of humans and simultaneously one of the most misunderstood.
Several types of psoriasis exist, each with unique signs and symptoms. These include:
Plaque psoriasis psoriasis vulgaris is the most common form of psoriasis. It causes dry, red skin lesions plaques covered with silvery scales. The plaques itch or feel sore and may occur anywhere on your body. About 80 of people who develop psoriasis have plaque psoriasis. Nail psoriasis produces a variety of changes in the appearance of finger and toe nails pitting, abnormal nail growth, discoloration. Psoriatic nails may become loose and separate from the nail bed onycholysis. Severe cases may cause the nail to crumble.
Scalp psoriasis occurs in at least half of all people with psoriasis. It can range from very mild with fine scaling to very severe with thick, crusted plaques.
Guttate psoriasis primarily affects people younger than 30 and is usually triggered by a bacterial infection such as strep throat. It is characterized by numerous small oval spots that appear over large areas of the body, such as the trunk, limbs, and scalp.
Inverse or Flexural psoriasis mainly affecting the skin in the armpits, groin, under the breasts and around the genitals. It appears as smooth inflamed patches of skin and is aggravated by friction and sweat.
Pustular psoriasis appears as raised bumps that are filled with non-infectious pustules. Yellow round pustules appear on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet, or generalised with widespread patches occurring randomly on any part of the body. They gradually turn brown and are shed as scales reach the surface. Generalized pustular psoriasis can also cause fever, chills, severe itching, weight loss and fatigue.
Erythrodermic psoriasis is the least common type of psoriasis but very serious and may require admission to hospital. Erythrodermic psoriasis can cover entire body with a red, peeling rash that can itch or burn intensely. This form of psoriasis can be fatal, as the extreme inflammation and exfoliation disrupt the body s ability to regulate temperature and for the skin to perform barrier functions.
Psoriatic arthritis is condition that causes deterioration, pain, and stiffness in the joints. Symptoms range from mild to severe. Psoriatic arthritis most commonly involves the fingers and toes. Joints in the neck, back, knees, ankles, and other areas also may be affected. In addition to being painful and stiff, the involved areas usually feel hot. Although the disease usually isn t as crippling as other forms of arthritis, it can cause stiffness and progressive joint damage that in the most serious cases may lead to permanent deformity. About 10-15 of people who have psoriasis also have psoriatic arthritis.
arm covered with plaque psoriasis Psoriasis treatment
Today, there are many different treatments available to help control psoriasis. No single treatment works for everyone. The goal is to find a treatment that works the best with the fewest side effects. One of the first principles of psoriasis treatment is to not create anything worse than the disease. Currently, there is no cure for psoriasis, but many different therapies can reduce, or nearly stop, their symptoms.
In addition to traditional treatments Topical treatment, Phototherapy, Systemic treatment the use of alternative psoriasis treatments are becoming more common as more and more people choose to treat their condition in more nontraditional ways. They have become tired of finding a traditional therapy that works, or may be concerned about the side effects many of those therapies produce. Alternative psoriasis treatments are in most cases perfectly safe and include:
Acupuncture, Ayurveda, Osteopathy, Climatotherapy, Diet, Dietary Supplements, Homeopathy, Water Therapies Balneotherapy, Heliotherapy, Phytotherapy, Thalassotherapy, Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatments, Meditation and Relaxation, Herbology, Hypnosis, Moisturizing Products, Magnets, Epsom salt.
What Are Discolored Skin Patches.
Irregular areas in which there are changes in skin
color are a common problem with a wide array of potential causes. You may have
changes in the pigmentation of a certain area of your skin due to a difference in
the level of melanin it contains. Melanin is the substance that provides color
to the skin and protects it from the sun.
Not sure what that rash is. Take a picture and send it into an online dermatologist
An infection or inflammatory problem can cause skin
color changes. Also, mottled skin can be caused by changes in blood vessels
under the skin. These changes can be genetic, caused by injury, or simply due
How Are Discolored Skin Patches Evaluated.
You should see your doctor if you have any lasting changes in
your skin color. Also see your doctor if you notice a new mole or growth on
your skin, or if an existing mole or growth has changed in size or appearance.
Your doctor will ask you a series of questions about your skin changes and may
order tests to determine why your skin has irregular coloring.
You may be asked about your normal skin color, when you
first noticed the skin color change, and whether the change happened slowly or
quickly. Is the change getting progressively worse. Where are the patches of
changed skin located. How are they distributed on your body.
Sunburns, other burns, and other skin injuries are also
important to discuss with your doctor. Similarly, it s important to tell him or
her if you are pregnant or taking any hormone treatments. All these factors may
play a role in your skin changes.
Your doctor may want to sample biopsy a small section of
the affected skin to examine under a microscope for the presence of cancerous
cells. Your doctor may also look at your skin under an ultraviolent light
called a Wood s lamp to more closely examine skin color changes, or to check
for the presence of bacteria. Blood tests may be necessary to check for conditions
that cause a change in skin color, such as hemochromatosis a genetic disease
that results in too much iron in the body.
It is important to tell your doctor about any other symptoms
you are experiencing along with patchy skin color.
What Causes Discoloration of Skin.
There are many potential causes of patchy skin color, ranging
You can damage your skin with sunburn or another kind of
burn, and the burn may heal with scar tissue that is a different color. You may
have applied sunscreen in an incomplete manner, leading to differently tanned parts
of your skin. Medications can make your skin more sensitive to the sun and more
likely to turn red or burn. Radiation therapy may also cause a kind of burn and
change the color of your skin.
Infections can cause localized changes in skin color. Cuts
and scrapes can develop infections that turn the surrounding skin red or white
and change the texture of the skin. Erythrasma
is a chronic skin infection caused by bacteria that causes pink skin with
brownish flaky patches and wrinkling.
Tinea versicolor and ringworm are infections caused by different
types of fungi. These fungal infections can cause patches of skin to turn
white, pink, tan, or brown and scaly. The patches can occur all over the body,
depending on the exact type of fungus.
Autoimmune Diseases and Allergies
Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus erythematosus and
dermatomyositis, can also cause changes in skin color. Eczema is a type of
hypersensitivity reaction allergy that can cause red, scaly patches that
ooze. Related to eczema, pityriasis alba can cause dry, white patches on the
A wide variety of rashes, such as dermatitis herpetiformis,
contact dermatitis, poison ivy rashes, and others can be caused by an allergic
reaction. Scleroderma can create thick, shiny patches of skin. Vitiligo is a
condition in which cells that produce melanin are attacked by the immune system,
leaving behind patches of skin with no color at all.
Hormonal changes, especially during pregnancy, can cause
skin color changes. Melasma, or chloasma, can cause dark patches on the face,
often called the mask of pregnancy.
Birthmarks are also a cause of skin color changes. Café-au-lait
spots are light-colored spots on the skin. A few café-au-lait spots are
perfectly normal, but more than six may be an indicator of neurofibromatosis a
genetic disorder that negatively affects the growth and formation of nerve
Moles are brown spots that can appear on the skin at birth.
Changes in the size or shape of these spots can signal trouble, and should be
Mongolian blue spots are bluish patches that can appear on
the backs of babies and young children, usually of Asian descent. They are
harmless and often fade over time.
Port-wine stains are a type of birthmark caused by swollen
blood vessels. They are usually flat and appear pink or red in color.
Cancer can change skin color or texture, and any moles or other
rapidly changing skin lesions should be examined by a doctor.
What Is the Long-Term Outlook for Discolored Skin Patches.
Many skin changes are harmless. Some, such as a small
infection, require only simple treatment. Other causes may be more severe and
require ongoing treatment. Skin cancer is very serious and may require surgery
and chemotherapy to treat. It is important to check with your doctor if you notice
rapid or bothersome texture or color changes in your skin.
scaly red patches on my arms. ?

About a year and a half ago I noticed this round, red, scaly patch on my arm and also on the back of one leg. Share this:Scaly area on armHi.
Symptoms of most rashes cause red, scaly as well as itchy at the affected area. These infections may manifest these scaly skin patches on arms, back, Causes.
What's Wrong With My Skin? 38 Causes of Discolored Skin Patches
Video embedded A reddish, scaly rash often located over the surfaces of the elbows, knees, scalp, Scaly patches of skin produced by fungal, viral, or bacterial infection.
I have been getting these small round scaly spots for no reason i can face back, or arm. which starts with a single scaly, red and slightly itchy spot.

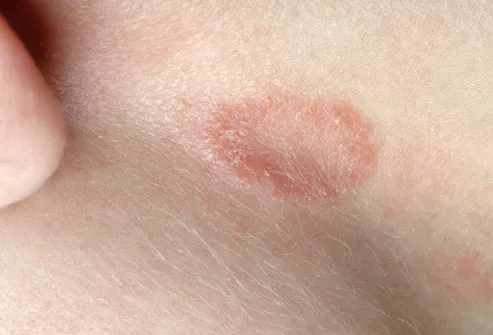
Authoritative facts about the skin from DermNet New Zealand. Psoriasis-like symmetrical or erythrodermic scaly rash; Orange-red hue; Scaly patches on arms.